 By Seth Woolcock and Erick Lauber
By Seth Woolcock and Erick Lauber
If you’re like most parents, you’re probably encouraging your kids to get into sports. I was encouraged like that. So was Dr. Lauber. You probably think you’re helping them avoid dangers, like drug addiction, obesity, teen pregnancy…
My friends and I were always playing backyard football, competing with sports video games, diving into fantasy leagues or consuming all the sports on television we could.
Never did it dawn on our parents that they might be creating a problem: an obsession with sports.
By the time we got to college we were playing fantasy sports competitively, but this included betting on the games. We extended our competitiveness into late night poker games. It started out as fun, but gradually winning became more about the money than the pride. We eventually started betting more: our fantasy league buy-ins became $50 rather than $20. Our poker buy-ins went from $10 to $30 and then $70.
I confess once I saw my friends attempting to gamble on just about everything, I stepped back. They were so consumed for a while they were making weekly casino trips – while poor college students! They were also making sports bets on teams for games years down the road – for hundreds of dollars.
Luckily, most of my friends eventually realized this was not a good hobby for them. But only after losing thousands of dollars.
Unfortunately, our state, Pennsylvania just officially declared sports gambling legal. I’m afraid for my friends. Here is what you need to know to make sure your kid doesn’t fall victim to a sports gambling addiction.
What did Pennsylvania (and maybe your state) do?
The new Pennsylvania law permits wagering “by any system or method,” including in person, on the internet and mobile. This means that while a person can go to registered casinos to place a bet on sports, they can also use their phone, tablet, computer or other device to make bets (as long as they are within the state borders.)
What can people legally bet on?
With the law change, people can legally bet on just about every sport. Wagering can be placed on popular sports in the U.S. such as football, baseball or basketball, but people can also bet on more obscure sports such as cricket, Formula 1 racing and golf.
While people can still make traditional wagers, such as betting against the spread or taking the over or under, they can also bet on just about anything with the new trend of “prop bets.” For example, they can now bet on the length of the national anthem, whether the coin toss is heads or tails, and whether there will be a rain delay or not? Yes, people can now bet on pretty much anything.
What are the legal requirements to make a wager?
Anyone over the age of 21 can legally bet on sports in Pennsylvania. The key word here is, “legally.” While it is still “illegal” to bet on sports while you are underage, it is still not difficult to do so. Take it from a college student – it is similar to drinking underage. If you want to do it, someone will help you out. By the way, did you know that 11% of the US’s entire alcohol output every year is drunk by 12-19 year olds? I’m guessing the same will be true for sports gambling pretty soon.
What is the deal with daily fantasy sports apps, such as Fan Dual and Draft Kings?
Fantasy sports is usually a season long game held between a league of people who pick rosters of players. The most popular sport is currently the NFL. Friends make points off of certain players, such as their yards per game, receptions and touchdowns.
The winner generally is the person with the best players throughout the entire season. While many fantasy football league winners receive nothing but bragging rights, some win a few thousand dollars. It’s big league betting in some circles.
Daily fantasy sports, or “DFS” is similar. But instead of taking place throughout an entire season, it is condensed down into a single day or week. So, while bettor doesn’t have to commit serious time to play a DFS app, it is still very easy to commit large amounts of money.
Many of these games/apps “sell” themselves by guaranteeing prize pools, “cash games”, Head-to-Head matchups and 50/50 games. Some now offer to match a newbie’s initial investment! The appeal these games/apps is growing from year to year.
So, how is this harmful?
Presently, 2.6% of the U.S. population has a gambling addiction. Over 50 percent of these 10 million Americans are between the ages of 16 to 24. They are by far the most affected age group.
Of the 10 million people who have this issue, over 50 percent of them fall between the age range of 16-24. They are by far the most affected age group, according to the North American Foundation for Gambling Addiction Help.
Sports betting isn’t always a problem, but gambling addiction occurs once gambling behavior begins to either cause distress, become a habit, leads to financial stress or disturbs everyday life and functioning.
DFS companies are spending millions to advertise to your kid. The risk is only growing larger. Educate yourself and your kids. I’m betting teenage “bankruptcy” is only going to grow. Pun intended.
Here are some helpful links for more information:
North American Foundation for Gambling Addiction Help
How the Brain Gets Addicted to Gambling
https://kidshealth.org/en/teens/gambling.html
450,000 children aged between 11 and 15 are gambling on a weekly basis…





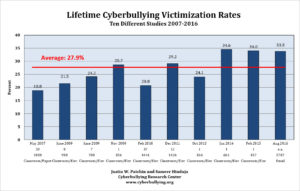

 By Seth Woolcock
By Seth Woolcock
 By Katie Mest
By Katie Mest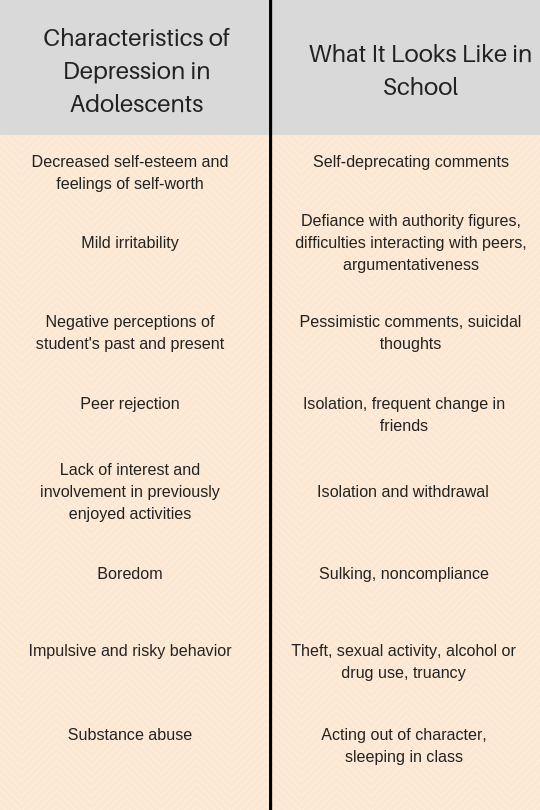

 By Lily Whorl and Erick Lauber
By Lily Whorl and Erick Lauber

 By Erick Lauber
By Erick Lauber
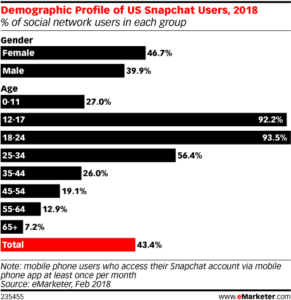

 By Morgan Rihn and Erick Lauber
By Morgan Rihn and Erick Lauber